My Assistant

My assistant
More Posts from T-b-a-blr-blog and Others

Gram staining
![[17 Dec 2017] (i Thought I’d Posted But It’s Not Appearing? ):) So Sorry For The Lack Of Original](https://64.media.tumblr.com/f1721a96c8d90aac046d6f8734faf5cd/tumblr_p13ywgKXmD1vusjcpo1_500.jpg)
[17 Dec 2017] (i thought i’d posted but it’s not appearing? ):) so sorry for the lack of original posts all these months! school has been so tough & i’ve just completed my mid-sem assessments & it’s finally my break! can’t wait to unwind and catch up on my sleep ;-;

CAMP test for the identification of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B).
(A) Streptococcus (group B) shows a positive CAMP reaction arrow-shaped zone of enhanced hemolysis .
(B) Streptococcus pyogenes (group A) shows a negative reaction when inoculated at a right angle to
© Staphylococcus aureus.
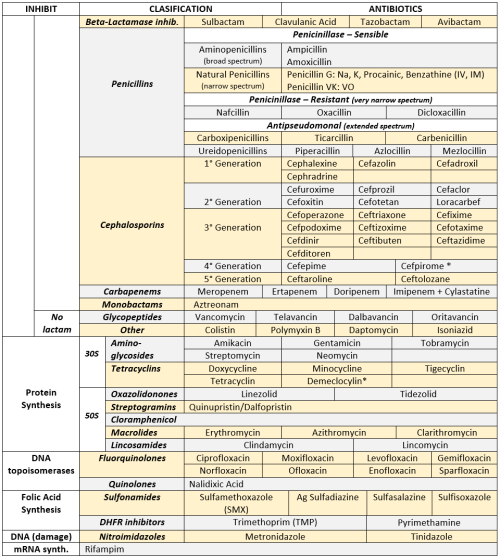
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET :)
Also, REMEMBER!!!!
* Sulfonamides compete for albumin with:
Bilirrubin: given in 2°,3°T, high risk or indirect hyperBb and kernicterus in premies
Warfarin: increases toxicity: bleeding
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Suceptible:
Natural Penicillins (G, V, F, K)
Aminopenicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin)
Antipseudomonal Penicillins (Ticarcillin, Piperacillin)
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Resistant:
Oxacillin, Nafcillin, Dicloxacillin
3°G, 4°G Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
* Penicillins enhanced with:
Clavulanic acid & Sulbactam (both are suicide inhibitors, they inhibit beta-lactamase)
Aminoglycosides (against enterococcus and psedomonas)
* Aminoglycosides enhanced with Aztreonam
* Penicillins: renal clearance EXCEPT Oxacillin & Nafcillin (bile)
* Cephalosporines: renal clearance EXCEPT Cefoperazone & Cefrtriaxone (bile)
* Both inhibited by Probenecid during tubular secretion.
* 2°G Cephalosporines: none cross BBB except Cefuroxime
* 3°G Cephalosporines: all cross BBB except Cefoperazone bc is highly highly lipid soluble, so is protein bound in plasma, therefore it doesn’t cross BBB.
* Cephalosporines are "LAME“ bc they do not cover this organisms
L isteria monocytogenes
A typicals (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia)
M RSA (except Ceftaroline, 5°G)
E nterococci

* Disulfiram-like effect: Cefotetan & Cefoperazone (mnemonic)
* Cefoperanzone: all the exceptions!!!
All 3°G cephalosporins cross the BBB except Cefoperazone.
All cephalosporins are renal cleared, except Cefoperazone.
Disulfiram-like effect
* Against Pseudomonas:
3°G Cef taz idime (taz taz taz taz)
4°G Cefepime, Cefpirome (not available in the USA)
Antipseudomonal penicillins
Aminoglycosides (synergy with beta-lactams)
Aztreonam (pseudomonal sepsis)
* Covers MRSA: Ceftaroline (rhymes w/ Caroline, Caroline the 5°G Ceph), Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Linezolid, Tigecycline.
* Covers VRSA: Linezolid, Dalfopristin/Quinupristin
* Aminoglycosides: decrease release of ACh in synapse and act as a Neuromuscular blocker, this is why it enhances effects of muscle relaxants.
* DEMECLOCYCLINE: tetracycline that’s not used as an AB, it is used as tx of SIADH to cause Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (inhibits the V2 receptor in collecting ducts)
* Phototoxicity: Q ue S T ion?
Q uinolones
Sulfonamides
T etracyclines

* p450 inhibitors: Cloramphenicol, Macrolides (except Azithromycin), Sulfonamides
* Macrolides SE: Motilin stimulation, QT prolongation, reversible deafness, eosinophilia, cholestatic hepatitis
* Bactericidal: beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems), aminoglycosides, fluorquinolones, metronidazole.
* Baceriostatic: tetracyclins, streptogramins, chloramphenicol, lincosamides, oxazolidonones, macrolides, sulfonamides, DHFR inhibitors.
* Pseudomembranous colitis: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, Lincomycin.
* QT prolongation: macrolides, sometimes fluoroquinolones

Penicillin

Penicillin is a widely used antibiotic prescribed to treat staphylococci and streptococci bacterial infections.
beta-lactam family
Gram-positive bacteria = thick cell walls containing high levels of peptidoglycan
gram-negative bacteria = thinner cell walls with low levels of peptidoglycan and surrounded by a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer that prevents antibiotic entry
penicillin is most effective against gram-positive bacteria where DD-transpeptidase activity is highest.
Examples of penicillins include:
amoxicillin
ampicillin
bacampicillin
oxacillin
penicillin
Mechanism(s)
Penicillin inhibits the bacterial enzyme transpeptidase, responsible for catalysing the final peptidoglycan crosslinking stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Cells wall is weakened and cells swell as water enters and then burst (lysis)
Becomes permanently covalently bonded to the enzymes’s active site (irreversible)


Alternative theory: penicillin mimics D-Ala D-Ala

Or may act as an umbrella inhibitor

Resistance
production of beta-lactamase - destroys the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and makes it ineffective (eg Staphylococcus aureus - most are now resistant)
In response, synthetic penicillin that is resistant to beta-lactamase is in use including egdicloxacillin, oxacillin, nafcillin, and methicillin.
Some is resistant to methicillin - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Demonstrating blanket resistance to all beta-lactam antibiotics -extremely serious health risk.

Stuff in my Office
From 1930. This well-dressed young scientist is experimenting with The Air. Exactly what he is doing is a mystery.
July 25 …. I finally get it! He’s holding an eye dropper with a bulb on the end. I thought it was a pair of chopsticks! He’s picking up pieces of paper using the vacuum from squeezing the bulb! Still very formal, though …


Medically Important Fungi
Influenza
Happy flu season! I’ve just been stuck inside for 5 days with a mild case, so this is a bit bitter
There are 3–5 million cases of flu per year, and ~375,000 deaths, usually in older, younger, and immunocompromised individuals.
Enveloped, Single-stranded RNA virus
First identified in 1933, but existed long before
Generally considered an infection of the bronchi
so effectively a form of bronchitis – i.e. it causes inflammation of the bronchi
There are 3 types - A, B and C
B & C appear restricted to humans
C is less common
A is found in wide range of species including pigs and poultry as well as man
Type A appears to be responsible for more severe disease

Basics
Transmission by aerosols
Incubation ~2 days
Contagious during first 3-5days of illness
Symptoms – fever, myalgia, headache, dry cough, sore throat, aches, fatigue
Recovery ~7-10 days for most
Complications – most frequent = secondary bacterial pneumonia, rarely = viral pneumonia, myocarditis, encephalitis
No specific treatment
Vaccination for high risk groups including the elderly, health care workers, those with underlying respiratory conditions.
Avian
The main reservoir is wildfowl that are resistant to the disease
doesn’t usually affect animals other than poultry and pigs
However some transfer events occur
Seasonal
Incidence highest in winter
Strains vary from year to year - hard to predict and vaccinate (this year’s vaccine has been pretty rubbish)
Pandemic
Can be caused by any strain that has not been seen in the human population for many years
New strains evade the herd immunity that exists to previously encountered strains
1918 /19 –( Spanish) estimated 40-50 million deaths worldwide
1957 – Influenza A/H1N1 (Asian)
1968 – Influenza A/H3N2 (Hong Kong)
Eventually the virus runs out of susceptible hosts and the epidemic fizzles out
Experts generally agree another pandemic is inevitable, and may be imminent – maybe we have had some minor pandemics
16000 confirmed H1N1 deaths in 2009 affecting over 200 countries
Consensus is that the prompt action of the Hong Kong authorities probably prevented a pandemic in 1997
The prediction is scary - for industrialised countries they predic 1.0 – 2.3 million hospitalisations
280,000-650,000 deaths
in two years
A network of 112 centres monitor flu isolates to identify unusual strains that can then be examined further
The WHO has a Pandemic Preparedness Plan in place http://www.who.int/influenza/preparedness/pandemic/en/
Diagnosis
Generally based on GP diagnosis
Virus isolation / virus demonstration from nasopharyngeal secretions during acute phase
Demonstration of viral antigen in secretions
Antibody rise using paired sera ( 1st sample taken between days 1-3 of illness, 2nd taken around day 12 of illness) by haemagglutination inhibition or complement fixation test
Molecular methods evolving rapidly – in particular in response to the recent epidemic/pandemic strains emerging
A range of respiratory illnesses have the same symptoms, only laboratory testing can confirm the aetiological agent
Treatment/Vaccination
In the UK NICE argue that immunisation against predicted strains is the best form of defence – traditionally focused on the elderly and those with underlying lung problems, but recently started rolling out a childhood vaccine (nasal spray)
Vaccines generally based on the H & N surface structures which mutate, however hopes of an M protein based vaccine which will give longer lasting protection raised recently
Antivirals
Antivirals not recommended in otherwise healthy people (amantadine should not be used at all) - should ride it out
However when incidence reaches a certain level zanamivir and oseltamivir should be used in those considered high risk for the development of complications – PROVIDED THAT TREATMENT IS STARTED WITHIN 48 HOURS OF ONSET OF SYMPTOMS
Resistance is becoming an issue
Normal Flora
Blood, Spinal Fluid, Urine: sterile
Cutaneous surfaces (urethra, outer ear included): Staph epidermidis, Staph aureus, Corynobacteria (dyphteroids),Streptocci, Candida spp
Nose: Staph aureus, Staph epidermidis, dyphteroids, assorted streptococci
Gingival crevices: anaerobes = Bacterioides/Prevotella, Fusobacterium, Streotococci, Actinomyces
Oropharynx: Viridans group (alpha hemolytic strep), Neisseria (non pathogenic), H. influenzae (non typeable, meaning, w/o capsule), Candida albicans
Stomach: none
Breast-fed babies colon: microaerophilic/anaerobic = Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, streptococci.
Adult Colon: microaerophilic/anaerobic = Bacteroides/Prevotella, E.coli, Bifidobacterium, Eubacterium, Fusobacterium, Gram- anaerobic rods, Lactobacillus, E.faecalis, streptococci
Vagina: Lactobacillus, streptococci, diphteroids, yeasts, Veillonella, Gram- rods
-
 bolioptics liked this · 6 years ago
bolioptics liked this · 6 years ago -
 ladytitanslayer liked this · 6 years ago
ladytitanslayer liked this · 6 years ago -
 ferventcore liked this · 6 years ago
ferventcore liked this · 6 years ago -
 felunax liked this · 6 years ago
felunax liked this · 6 years ago -
 ajoyfulnovelty liked this · 6 years ago
ajoyfulnovelty liked this · 6 years ago -
 littlekittenniceandsoft-blog liked this · 6 years ago
littlekittenniceandsoft-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 13-reasons-why-photos-blog liked this · 6 years ago
13-reasons-why-photos-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 alchemyparadox liked this · 6 years ago
alchemyparadox liked this · 6 years ago -
 flamingojingo liked this · 6 years ago
flamingojingo liked this · 6 years ago -
 astudyinshadows reblogged this · 6 years ago
astudyinshadows reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 studywithcharlie liked this · 6 years ago
studywithcharlie liked this · 6 years ago -
 coolnaronkfan-blog liked this · 6 years ago
coolnaronkfan-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 thefuturelawyer reblogged this · 6 years ago
thefuturelawyer reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 thefuturelawyer liked this · 6 years ago
thefuturelawyer liked this · 6 years ago -
 fadingsludgebanditopera-blog liked this · 6 years ago
fadingsludgebanditopera-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 disneypassholder-blog liked this · 6 years ago
disneypassholder-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 intrinsicstudy reblogged this · 6 years ago
intrinsicstudy reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 flamingojingo reblogged this · 6 years ago
flamingojingo reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 scrappedacc liked this · 6 years ago
scrappedacc liked this · 6 years ago -
 schmidthappens93 liked this · 6 years ago
schmidthappens93 liked this · 6 years ago -
 procrastinatingqueenhch-blog liked this · 6 years ago
procrastinatingqueenhch-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 d4rk3r0 liked this · 6 years ago
d4rk3r0 liked this · 6 years ago -
 anauve reblogged this · 6 years ago
anauve reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 anauve liked this · 6 years ago
anauve liked this · 6 years ago -
 starry-eyed-butch liked this · 6 years ago
starry-eyed-butch liked this · 6 years ago -
 2gymnast1 liked this · 6 years ago
2gymnast1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 stupidnumber4-blog liked this · 7 years ago
stupidnumber4-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 casualnightmarekitty liked this · 7 years ago
casualnightmarekitty liked this · 7 years ago -
 upsidedownknight reblogged this · 7 years ago
upsidedownknight reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 upsidedownknight liked this · 7 years ago
upsidedownknight liked this · 7 years ago -
 metoxil liked this · 7 years ago
metoxil liked this · 7 years ago -
 lilynightingale liked this · 7 years ago
lilynightingale liked this · 7 years ago -
 bronwyn-writes liked this · 7 years ago
bronwyn-writes liked this · 7 years ago -
 thedarkestpegusus reblogged this · 7 years ago
thedarkestpegusus reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mralenko liked this · 7 years ago
mralenko liked this · 7 years ago -
 astudyinshadows reblogged this · 7 years ago
astudyinshadows reblogged this · 7 years ago