195 posts
Latest Posts by t-b-a-blr-blog - Page 6
Pneumonia
“Pneumonia is called the old man’s friend because, left untreated, the sufferer often lapses into a state of reduced consciousness, slipping peacefully away in their sleep, giving a dignified end to a period of often considerable suffering.” -Dr John Pillinger
Pneumonia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, the 6th largest cause of death in the USA. It is also economically costly in antibiotics, time off work, and hospitalisation
In half the cases the cause is not identified
In those where a cause is identified, S. pneumoniae is the most common cause
The reservoir is usually humans (oneself or a contact)
spread is through respiratory droplets
Community acquired eg Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae
Noscomial (hospital acquired) eg Enterobacteriaceae, Staphylococcus aureus, Anaerobes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Many patients have an underlying condition, e.g. bronchitis, asthma, a viral infection, tumours
Characterised by the alveolar sacs filling up with pus, giving rise to a purulent sputum
Symptoms
Results in chest tightness or pain, difficulty in breathing, fever or hypothermia, reduced blood oxygen, coughing to clear mucus, chest will sound “dull” when tapped, tachypnea, tachycardia (>100 bpm) or bradycardia (< 60 bpm), central cyanosis, altered mental status.

Streptococcus pneumoniae: Rust-colored sputum
Pseudomonas, Haemophilus, and pneumococcal species: May produce green sputum
Klebsiella species pneumonia: Red currant-jelly sputum
Anaerobic infections: Often produce foul-smelling or bad-tasting sputum
Diagnosis
X-ray showing infiltrates
Elevated temperature
Changes in WBC counts
Culture confirmation
Serum chemistry panel
Arterial/venous blood gas
Serum free cortisol value and lactate level

Treatment
Intensive treatment, potentially to ITU level
Tailored antimicrobials if possible - limited options with viruses
Treatments include: analgesia and antipyretics, physiotherapy, bronchodilators and N-acetylcysteine, suctioning and bronchial hygiene, ventilation
Pathogenesis
Causative agents can enter the lungs through inhalation, aspiration, spread across mucous membrane (some viruses), haematogenous spread (occasionally, e.g. IV drug users with S. aureus septicaemia) and penetrating injury (rare).
Immune response is triggered in the lung and there are local defence factors in the respiratory secretions
Cilia, if functioning, will move material up the respiratory tract, but if damaged this physical defence is impaired
The lungs also have a resident macrophage population (alveolar macrophages) but they are of limited use against several respiratory pathogens that possess a capsule
some organisms can even replicate in these cells
Damage to the lung is caused by the microbes and the immune response
Enzymes released by the bacteria
Factors released by immune cells that cause local irritation and cell apoptosis
Systemic manifestations follow eg
Oxygen deprivation – thickening of the membranes reduces gas transfer
Systemic shock – especially with Gram-negative bacilli such as Haemophilus influenzae




Dr Warhol’s Periodic Table of Microbes
56. Ba. Bacillus
There are more than 300 species of Bacillus, which is a whole whopping load of microbes. Just to wrap your head around that number, if you talked about each one for 1 minute you’d be talking nonstop for 5 hours! Take that TedTalks!
Starting with the basics, these organisms found all over the world, predominantly in soil but microbes go where they please, so they have been found in undersea hydrothermal vents as well as in the stratosphere. They are rod-shaped and form spores.
Just to list a few of the most noteworthy and awesome Bacillus species:
Abyssalis: found more than a mile and a half down at the bottom of the South China Sea.
Anthracis: causative agent of Anthrax, the disease, not the band; death, disease, toxins, yahoo!
Azotofixans: fixes nitrogen.
Canaveralius: StarFleet Academy space bacteria living on the walls of the Kennedy Space Center!
Cereus: you get to play with this in General Microbiology, a pathogen causing foodborne illness.
Decolorationis: for you art history majors, isolated from decaying parts of a mural in the Roman necropolis in Carmona, Spain.
Megaterium: it can consume cave paintings.
Stratosphericus: found in high concentrations orbiting the Earth with satellites around 6 miles up!
Subtilis: the grass bacillus; used for industrial enzyme secretion.
Thuringiensis: absolutely famous for producing the BT toxin used as a natural insecticide.
Bacillus cells are Gram positive rods that measures about 1 micron wide by 4 to 10 microns long, but with more than 300 species you will see a range of sizes.
Everyone needs their own Periodic Table of Microbes from https://www.etsy.com/no-en/shop/WarholScience.
Copyright 2016 Warhol.

Stuff in my Office
From 1930. This well-dressed young scientist is experimenting with The Air. Exactly what he is doing is a mystery.
July 25 …. I finally get it! He’s holding an eye dropper with a bulb on the end. I thought it was a pair of chopsticks! He’s picking up pieces of paper using the vacuum from squeezing the bulb! Still very formal, though …




11.19.17
2 more days until break
Music mood: Mili - Miracle Milk

One possible cover design for The Book
Coming soon.

Me durning finals.

how am i always so behind in my work ??
(i do know the answer to this, it’s called procrastination lmao)

(Day 4/100 days of productivity) - Haemophilus Influenzae card!
Today was mostly spent working on research, textbooks, but and making flashcards like this for microbiology!

That’s why we have skin and immune system.

it’s technically kinda busy work but i still love it

Which Microbe Would You Be?
Buzzfeed has a quiz on what bacteria would you be, based on your personality.
I was a Salinicola salarius. (Which isn’t on my Periodic Table of Microbes!)
https://www.buzzfeed.com/grandon/which-bacteria-are-you-based-on-your-personality-3dk99?utm_term=.am4B9qO8B#.ab5oX2B0o
Follow on Twitter @warholScience

Sooo I’m studying microbiology 2:28 am because I’m a desperate bitch Microbiology + immunology = total final grade I got a 10 in my immunology test so I’m PRAYING for a 10 in microbiology so I can get a bIG BeauTiFul 10 on my final




• Microbiology cheat sheets for the comprehensive final. We were allowed two pages, front and back. I ended up getting a 95%! •
Antimicrobial Agents - Cell wall inhibitors
Based on mode of action • divided into families based on chemical structure
Modes of action Interference with:
cell wall synthesis
protein synthesis
nucleic acid synthesis
plasma membrane integrity
metabolic pathway
Inhibitors of Bacterial Cell Wall (peptidoglycan) Synthesis
The Beta-lactam Family
The Glycopeptides

Peptidoglycan is composed of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) repeat units, and amino acids. Each NAM is linked to peptide chain and the peptide chains are cross-linked.
β-lactams
Includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins (cephems), monobactams, and carbapenems.
class of broad-spectrum antibiotics containing a β-lactam ring
Bacterial transpeptidase enzymes are responsible for catalysing cross-linking of the peptide chains
β-lactam ring bind to these transpeptidases – this inhibits cross-linking between peptide chains and prevents synthesis of stable PG
Cell wall synthesis ceases and the bacterial cells eventually die due to osmotic instability or autolysis.

Glycopeptides
Polypeptide agents - basic structural elements amino acids
Vancomycin:
complexes with peptide portion of peptidoglycan’s precursor units
vancomycin is a large hydrophilic molecule able to form hydrogen bonds with the terminal D-alanyl-D-alanine moieties of the NAM/NAG-peptides
preventing PG transglycosylation reaction – PG precursor subunits (NAG-NAM+peptide) cannot be inserted into peptidoglycan matrix;
Vancomycin also alters bacterial-cell-membrane permeability and RNA synthesis
Uses: serious Gram positive infections e.g. MRSA wound infection
Adverse effects:
damage to auditory nerve
hearing loss (ototoxicity)
“Red man/neck” syndrome - rash on face, neck, upper torso
….and that is how viruses go about their non-lives!!
my biology professor at the end of a lecture about viruses, presumably, i wouldn’t know, i wasn’t paying attention, i’m using context clues here (via scienceprofessorquotes)

My assistant
This disease typically affects children because, well, kids are gross and have fewer inhibitions about sticking their poop hands in their mouth
Sketchy Medical on Enterobius vermicularis (via medschoolmanic)
If you cannot grasp what I have just explained, you should just leave and study economics!
Microbiology professor, first lecture (via scienceprofessorquotes)
Remember to use your sponge to replace any bacteria on your dishes accidentally removed by the act of eating.
Microbiology professor (via scienceprofessorquotes)









nasty moodboard
![[x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/955b3402836e292187e6435c26797c9d/tumblr_ohsjpvHnW61qiz5q7o1_500.jpg)
[x]

30 . 06 . 2017 Microbiology notes !!! Yesterday I took my physics final exam and it went great: I got a 27/30, which is way more than what I expected as Physics is one of my worst subjects. My next exam, microbiology, is in four days and I’m starting to feel a bit anxious about it as it’s a pretty tough exam but I’ll try to do my best !
Antimicrobial Agents - Inhibition of DNA and Protein Synthesis
Bacterial chromosome replication

DNA replication

Bacterial Topoisomerases
maintain DNA in appropriate state of supercoiling
cut and reseal DNA
DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) introduces negative supercoils
Topoisomerase IV decatenates circular chromosomes
these are the targets of the quinolone antibacterial agents
Quinolones
bind to bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV after DNA strand breakage
prevent resealing of DNA
disrupt DNA replication and repair
bactericidal (kill bacteria)
Fluoroquinolone is particularly useful against
Gram +ves: Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci
Gram -ves: Enterobacteriacea; Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Anaerobes: e.g. Bacteroides fragilis
many applications e.g. UTIs, prostatitis, gastroenteritis, STIs
Adverse effects
Relatively well tolerated
GI upset in ~ 5% of patients
allergic reactions (rash, photosensitivity) in 1 - 2% of patients

Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Macrolides
in 1952: Erythromycin was isolated as the first macrolide (Streptomyces erythreus)
Newer macrolides: clarithromycin, azithromycin
Structurally they consist of a lactone ring (14- to 16-membered) + two attached deoxy sugars
Mode of action
bind reversibly to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit
causes growing peptide chain to dissociate from ribosome → inhibiting protein synthesis
bacteriostatic (stops reproduction)

Macrolides’ spectrum of activity
good antistaphylococcal and antistreptococcal activity
treatment of respiratory & soft tissue infections and sensitive intracellular pathogens • e.g. Chlamydia, Legionella
Adverse effects
Generally well tolerated
nausea
vomiting
diarrhoea
rash
Aminoglycosides
large family of antibiotics produced by various species of Streptomyces (“mycin”) and Micromonospora (“micin”)
include: streptomycin, neomycin, kanamycin, gentamicins, tobramycin
Structure = linked ring system composed of aminosugars and an aminosubstituted cyclic polyalcohol
Mode of action of aminoglycosides
Bind irreversibly to 30S ribosomal subunit
disrupt elongation of nascent peptide chain
translational inaccuracy → defective proteins
bactericidal

Spectrum of activity
broad spectrum; mainly aerobic G-ve bacilli (e.g. P. aeruginosa)
used to treat serious nosocomial infections (hospital acquired infections)
First TB antibiotic
Used for cystic fibrosis
Adverse effects
all aminoglycosides have low Therapeutic Index (only a small amount needed to become toxic)
renal damage, ototoxicity, loss of balance, nausea
Without immunity, we’RE JUST BAGS OF NUTRIENTS!
Microbiology lecturer (via scienceprofessorquotes)
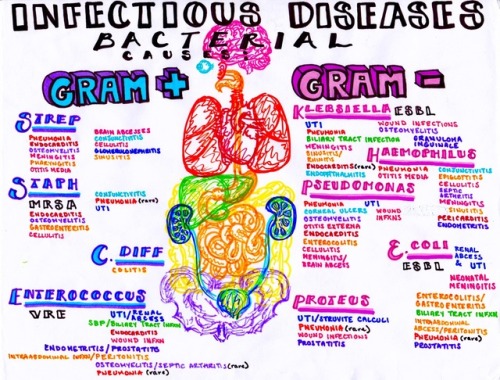
Infectious bacterial diseases and where to find them

That cell specialization…it’s pretty important.
(From our video)
![[17 Dec 2017] (i Thought I’d Posted But It’s Not Appearing? ):) So Sorry For The Lack Of Original](https://64.media.tumblr.com/f1721a96c8d90aac046d6f8734faf5cd/tumblr_p13ywgKXmD1vusjcpo1_500.jpg)
[17 Dec 2017] (i thought i’d posted but it’s not appearing? ):) so sorry for the lack of original posts all these months! school has been so tough & i’ve just completed my mid-sem assessments & it’s finally my break! can’t wait to unwind and catch up on my sleep ;-;



Review sheets from my microbiology exam last Monday 🔬

Who wants a box of chocolates when you can have a petri dish of bacteria?